Quick Changeover
Changeover is the process of modifying a line or production sequence in order to produce a different product. It usually refers to a tool or “die” change, or some other form of equipment modification or swap. Changeover time is the time between the last good piece of one run to the first good piece of the next run. Quick changeover is the discipline of making the changeover process as efficient as possible.
Changeover time is downtime for any line and therefore a perfect target for operational improvement. When Taichi Ohno started work on Lean at Toyota in the 1950s, one of the biggest causes of downtime was when they made die changes to stamp different parts for vehicles. These changes could sometimes take hours or days. They started working on a program called Single Minute Exchange of Die (SMED). The target was to do a changeover in less than 10 minutes (therefore “single minute”, meaning 9 or less). Since then the terminology has shifted to Quick Changeover its more translatable and changeover can apply to any form of changing a production line or sequence (or even service delivery for example) in order to produce something new.
Quick changeover makes small lot production possible, which in turn
- Improves flexibility to respond to customer needs
- Reduces WIP and finished goods inventory and associated space requirement
- Improves quality – less scrap and rework
- Increases machine capacity and Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Four stage, nine step quick changeover process
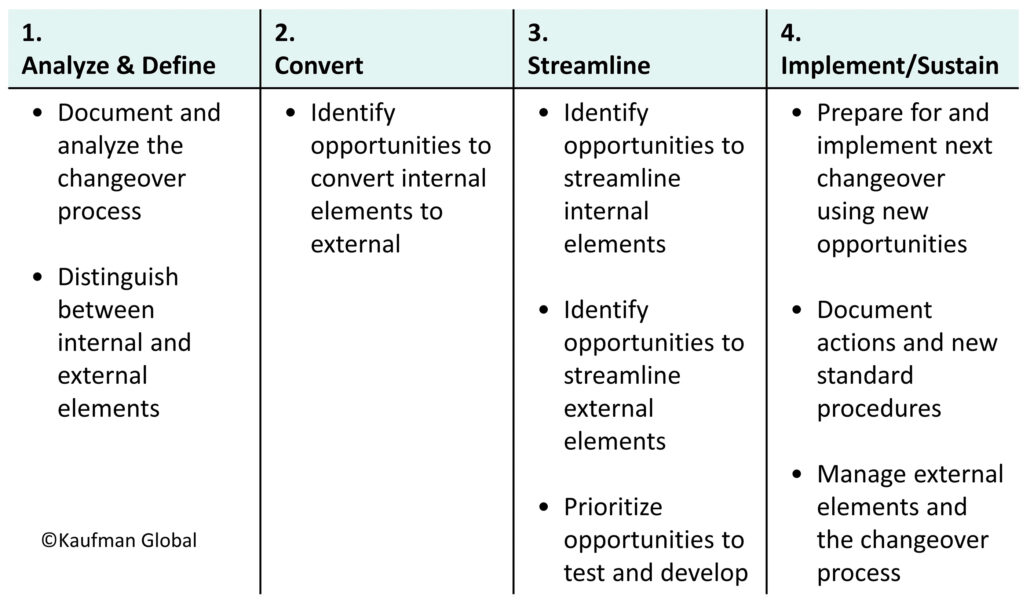
Quick changeover is generally associated with manufacturing operations, but its principles apply equally to non-manufacturing operations. Examples of non-manufacturing applications:
- Planning / marshaling / connecting vehicles (tractors, trailers, containers, boxcars) for transportation and delivery
- Software upgrades and conversions
- Maintaining and changing office equipment
- Facility relocations and modifications
- New product launches and events
Quick changeover attacks the waste of waiting as described in the Lean Waste Wheel.
« Back to Glossary Index